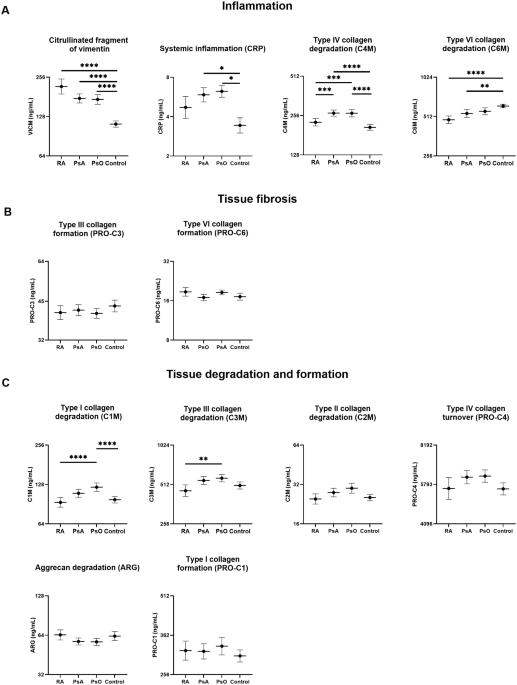
McInnes, I. B. & Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 55, 2255–2270 (2011).
Ritchlin, C. T., Colbert, R. A. & Gladman, D. D. Psoriatic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 957–70 (2017).
Google Scholar
Holm Nielsen, S. et al. Differentiating patients with psoriasis from psoriatic arthritis using collagen biomarkers. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.55563/clinexprheumatol/jmt9jv (2022).
Google Scholar
Thudium, C. S. et al. The Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor baricitinib reduces biomarkers of joint destruction in moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 22, 1–11 (2020).
Google Scholar
Karsdal, M. A. Type I collagen. In Biochemistry of Collagens, Laminins and Elastin: Structure, Function and Biomarkers (ed. Karsdal, M. A.) 1–389 (Elsevier, 2019).
Maijer, K. I. et al. Neo-epitopes-fragments of cartilage and connective tissue degradation in early rheumatoid arthritis and unclassified arthritis. PLoS ONE 11, 1–12 (2016).
Google Scholar
Yurchenco, P. D., Amenta, P. S. & Patton, B. L. Basement membrane assembly, stability and activities observed through a developmental lens. Matrix Biol. 22, 521–538 (2004).
Google Scholar
Danielsson, F. et al. Vimentin diversity in health and disease. Cells 7, 1–38 (2018).
Google Scholar
Drobinski, P. J. et al. In contrast to Anti-CCP, MMP-degraded and citrullinated vimentin (VICM) is both a diagnostic and a treatment response biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 1–12 (2022).
Google Scholar
Groen SS, Nielsen SH, Bay-Jensen AC, et al. Are Serological Protease-mediated Peptides of Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation the New Disease Activity Biomarkers in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 74 (2022).
Siebuhr, A. S. et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-dependent turnover of cartilage, synovial membrane, and connective tissue is elevated in rats with collagen induced arthritis. J. Transl. Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-195 (2012).
Google Scholar
Grillet, B. et al. Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritis: Towards precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 19, 363–377 (2023).
Google Scholar
Bay-Jensen, A. C. et al. Tissue metabolite of type I collagen, C1M, and CRP predicts structural progression of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Rheumatol. 3, 1–10 (2019).
Google Scholar
Schett, G. et al. Collagen turnover biomarkers associate with active psoriatic arthritis and decrease with guselkumab treatment in a phase 3 clinical trial (DISCOVER-2). Rheumatol. Ther. 9, 1017–1030 (2022).
Google Scholar
Kim, K. S. et al. Expression levels and association of gelatinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 and collagenases MMP-1 and MMP-13 with VEGF in synovial fluid of patients with arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 31, 543–547 (2011).
Google Scholar
Jadon, D. R. et al. Serum bone-turnover biomarkers are associated with the occurrence of peripheral and axial arthritis in psoriatic disease: A prospective cross-sectional comparative study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 19, 1–10 (2017).
Google Scholar
Mezentsev, A., Nikolaev, A. & Bruskin, S. Matrix metalloproteinases and their role in psoriasis. Gene 540, 1–10 (2014).
Google Scholar
Drobinski, P. J. et al. Connective tissue remodelling is differently modulated by tocilizumab versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 23, 1–12 (2021).
Google Scholar
Thudium, C. S. et al. Bone phenotypes in rheumatology—There is more to bone than just bone. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 21, 1–20 (2020).
Google Scholar
Kjelgaard-Petersen, C. F. et al. Translational biomarkers and ex vivo models of joint tissues as a tool for drug development in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 70, 1419–1428 (2018).
Google Scholar
Bay-Jensen, A. C. et al. POS0006 identification of fibrotic and fibrolytic endotypes in rheumatic disease cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 81, 216 (2022).
Google Scholar
Bodur, H., Yilmaz, O. & Keskin, D. Hand disability and related variables in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 26, 541–4 (2006).
Google Scholar
Liphardt, A.-M. et al. Similar impact of psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis on objective and subjective parameters of hand function. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2, 734–40 (2020).
Google Scholar
Rydholm, M. et al. The relation between disease activity, patient-reported outcomes, and grip force over time in early rheumatoid arthritis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 1, 507–15 (2019).
Google Scholar
Stamm, T. A. et al. Moberg picking-up test in patients with inflammatory joint diseases: a survey of suitability in comparison with button test and measures of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 49, 626–32 (2003).
Google Scholar
Ng, C. L., Ho, D. D. & Chow, S. P. The Moberg pickup test: Results of testing with a standard protocol. J. Hand Ther. 12, 309–312 (1999).
Google Scholar
Durmus, D. et al. Michigan Hand Outcomes Questionnaire in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Relationship with disease activity, quality of life, and handgrip strength. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 26, 467–73 (2013).
Google Scholar
Ozer, P. K. et al. Ultrasound-defined remission for good functional status in rheumatoid arthritis. Indian J. Med. Res. 146, 230–6 (2017).
Google Scholar
Aletaha, D. et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 2569–81 (2010).
Google Scholar
Taylor, W. et al. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2665–73 (2006).
Google Scholar
Berlin, A. et al. The ageing joint-standard age- and sex-related values of bone erosions and osteophytes in the hand joints of healthy individuals. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 27, 1043–7 (2019).
Google Scholar
Ware, J. E. et al. Conceptualization and Measurement of Health for Adults in the Health Insurance Study: Vol. I, Model of Health and Methodology (Rand Corporation, 1980).
Craig, C. L. et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 35, 1381–95 (2003).
Google Scholar
Leeming, D. J. et al. A novel marker for assessment of liver matrix remodeling: An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detecting a MMP generated type I collagen neo-epitope (C1M). Biomarkers 16, 616–628 (2011).
Google Scholar
Bay-Jensen, A.-C. et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISAs) for metalloproteinase derived type II collagen neoepitope, CIIM–increased serum CIIM in subjects with severe radiographic osteoarthritis. Clin. Biochem. 44, 423–429 (2011).
Google Scholar
He, Y. et al. Development of a highly sensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay for quantification of aggrecanase-generated ARGS aggrecan fragments in serum. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 3, 100162 (2021).
Google Scholar
Barascuk, N. et al. A novel assay for extracellular matrix remodeling associated with liver fibrosis: An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for a MMP-9 proteolytically revealed neo-epitope of type III collagen. Clin. Biochem. 43, 899–904 (2010).
Google Scholar
Veidal, S. S. et al. Assessment of proteolytic degradation of the basement membrane: A fragment of type IV collagen as a biochemical marker for liver fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 4, 22 (2011).
Google Scholar
Veidal, S. S. et al. MMP mediated degradation of type VI collagen is highly associated with liver fibrosis–identification and validation of a novel biochemical marker assay. PLoS ONE 6, e24753 (2011).
Google Scholar
Bay-Jensen, A. C. et al. Circulating citrullinated vimentin fragments reflect disease burden in ankylosing spondylitis and have prognostic capacity for radiographic progression. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 972–980 (2013).
Google Scholar
Leeming, D. J. et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent serum assays (ELISAs) for rat and human N-terminal pro-peptide of collagen type I (PINP)–assessment of corresponding epitopes. Clin. Biochem. 43, 1249–1256 (2010).
Google Scholar
Nielsen, M. J. et al. The neo-epitope specific PRO-C3 ELISA measures true formation of type III collagen associated with liver and muscle parameters. Am. J. Transl. Res. 5, 303–315 (2013).
Google Scholar
Leeming, D. J. et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent serum assay specific for the 7S domain of collagen type IV (P4NP 7S): A marker related to the extracellular matrix remodeling during liver fibrogenesis. Hepatol. Res. 42, 482–493 (2012).
Google Scholar
Frimodt-Møller, M. et al. A marker of type VI collagen formation (PRO-C6) is associated with higher arterial stiffness in type 1 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 56, 711–712 (2019).
Google Scholar
Chung, K. C. et al. Reliability and validity testing of the Michigan Hand Outcomes Questionnaire. J. Hand Surg. 23, 575–587 (1998).
Google Scholar
Gudmann, N. S. et al. Type I and III collagen turnover is increased in axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Associations with disease activity and diagnostic capacity. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 35, 653–659 (2017).
Google Scholar
Groen, S. S. et al. Op0031 serological collagen biomarkers can differentiate patients with psoriasis from psoriatic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 81(23), 2–23 (2022).
Bay-Jensen, A. C. et al. Early changes in blood-based joint tissue destruction biomarkers are predictive of response to tocilizumab in the LITHE study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 18, 7–15 (2016).
Google Scholar
Bay-Jensen, A. C. et al. Effect of tocilizumab combined with methotrexate on circulating biomarkers of synovium, cartilage, and bone in the LITHE study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 43, 470–478 (2014).
Google Scholar
Hu, M. Y., Yang, Q. & Zheng, J. The association of psoriasis and hypertension: Focusing on anti-inflammatory therapies and immunological mechanisms. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 45, 836–40 (2020).
Google Scholar