Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D. & McInnes, I. B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 388, 2023–2038 (2016).
An, J., Nyarko, E. & Hamad, M. A. Prevalence of comorbidities and their associations with health-related quality of life and healthcare expenditures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 38, 2717–2726 (2019).
Google Scholar
Zeng, X. F., Zhu, S. L., Tan, A. C. & Xie, X. P. A systematic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis disease burden and quality of life in China. A systematic evaluation of studies on disease burden and quality of survival of rheumatoid arthritis in China. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine 13, 300–307 (2013). (2011).
Sokka, T., Abelson, B. & Pincus, T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 26, S35–61 (2008).
Google Scholar
Hu, K. et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis among rural residents aged 20–79 years and risk factors in Qiannan, Guizhou. China Public. Health. 35, 813–817 (2019).
Lo, J., Chan, L. & Flynn, S. A. Systematic review of the incidence, prevalence, costs, and activity and work limitations of amputation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, back pain, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury in the united States: A 2019 update. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 102, 115–131 (2021).
Google Scholar
Zhu, T. Y., Tam, L. S. & Li, E. K. Societal costs of rheumatoid arthritis in Hong Kong: a prevalence-based cost-of-illness study. Rheumatol. (Oxford). 50, 1293–1301 (2011).
Google Scholar
Deane, K. D. et al. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 31, 3–18 (2017).
Google Scholar
Gerlag, D. M. et al. EULAR recommendations for terminology and research in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: report from the study group for risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 638–641 (2012).
Google Scholar
Kim, K., Bang, S. Y., Lee, H. S. & Bae, S. C. Update on the genetic architecture of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 13, 13–24 (2017).
Google Scholar
Yamamoto, K., Okada, Y., Suzuki, A. & Kochi, Y. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis in Asia–present and future. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 11, 375–379 (2015).
Google Scholar
Sun, J. Analysis of risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis and its prevalence in middle-aged and elderly population in Luohe area of Henan Province. Chongqing Med. 46, 802–804 (2017).
Tobón, G. J., Youinou, P. & Saraux, A. The environment, geo-epidemiology, and autoimmune disease: rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 9, A288–292 (2010).
Google Scholar
Otsuki, T. et al. Immunological effects of silica and asbestos. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 4, 261–268 (2007).
Google Scholar
Alsaber, A. et al. Influence of ambient air pollution on rheumatoid arthritis disease activity score index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 17, 416 (2020).
Google Scholar
Jung, C. R., Hsieh, H. Y. & Hwang, B. F. Air pollution as a potential determinant of rheumatoid arthritis: A Population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Epidemiology 28 (Suppl 1), S54–S59 (2017).
Google Scholar
van Beers-Tas, M. H., Turk, S. A. & van Schaardenburg, D. How does established rheumatoid arthritis develop, and are there possibilities for prevention? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 29, 527–542 (2015).
Google Scholar
Kurreeman, F. et al. Genetic basis of autoantibody positive and negative rheumatoid arthritis risk in a multi-ethnic cohort derived from electronic health records. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 88, 57–69 (2011).
Google Scholar
Sparks, J. A. & Costenbader, K. H. Genetics, environment, and gene-environment interactions in the development of systemic rheumatic diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 40, 637–657 (2014).
Google Scholar
Lahiri, M. et al. Using lifestyle factors to identify individuals at higher risk of inflammatory polyarthritis (results from the European prospective investigation of Cancer-Norfolk and the Norfolk arthritis Register–the EPIC-2-NOAR Study). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 219–226 (2014).
Google Scholar
Hashimoto, M. et al. Periodontitis and Porphyromonas gingivalis in preclinical stage of arthritis patients. PLoS One. 10, e0122121 (2015).
Google Scholar
Lahiri, M., Morgan, C., Symmons, D. P. M. & Bruce, I. N. Modifiable risk factors for RA: prevention, better than cure? Rheumatol. (Oxford). 51, 499–512 (2012).
Google Scholar
Alpízar-Rodríguez, D., Pluchino, N., Canny, G., Gabay, C. & Finckh, A. The role of female hormonal factors in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. (Oxford). 56, 1254–1263 (2017).
Google Scholar
Yarwood, A., Huizinga, T. W. J. & Worthington, J. The genetics of rheumatoid arthritis: risk and protection in different stages of the evolution of RA. Rheumatol. (Oxford). 55, 199–209 (2016).
Google Scholar
van der Woude, D. Helm-van Mil, A. H. M. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors, and disease outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 32, 174–187 (2018). van der.
Google Scholar
de Hair, M. J. H. et al. Smoking and overweight determine the likelihood of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 1654–1658 (2013).
Google Scholar
Karlson, E. W. et al. Association of environmental and genetic factors and gene-environment interactions with risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken). 65, 1147–1156 (2013).
Google Scholar
Karlson, E. W. et al. Cumulative association of 22 genetic variants with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis risk. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 1077–1085 (2010).
Google Scholar
Messemaker, T. C., Huizinga, T. W. & Kurreeman, F. Immunogenetics of rheumatoid arthritis: Understanding functional implications. J. Autoimmun. 64, 74–81 (2015).
Google Scholar
Rakieh, C. et al. Predicting the development of clinical arthritis in anti-CCP positive individuals with non-specific musculoskeletal symptoms: a prospective observational cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 1659–1666 (2015).
Google Scholar
Scott, I. C. et al. Predicting the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and its age of onset through modelling genetic risk variants with smoking. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003808 (2013).
Google Scholar
Sparks, J. A. et al. Improved performance of epidemiologic and genetic risk models for rheumatoid arthritis serologic phenotypes using family history. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 1522–1529 (2015).
Google Scholar
van de Stadt, L. A., Witte, B. I. & Bos, W. H. Schaardenburg, D. A prediction rule for the development of arthritis in seropositive arthralgia patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 1920–1926 (2013). van.
Google Scholar
Bae, S. C. & Lee, Y. H. Alcohol intake and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a Mendelian randomization study. Z. Rheumatol. 78, 791–796 (2019).
Google Scholar
Hozumi, H. et al. Acute exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: mortality and its prediction model. Respir Res. 23, 57 (2022).
Google Scholar
van Boheemen, L. & van Schaardenburg, D. Predicting rheumatoid arthritis in At-risk individuals. Clin. Ther. 41, 1286–1298 (2019).
Google Scholar
Aletaha, D. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62, 2569–2581 (2010). (2010).
Pattison, D. J. et al. Dietary risk factors for the development of inflammatory polyarthritis: evidence for a role of high level of red meat consumption. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 3804–3812 (2004).
Google Scholar
Dupont, W. D. Power calculations for matched case-control studies. Biometrics 44, 1157–1168 (1988).
Google Scholar
Internal validation of predictive models. Efficiency of some procedures for logistic regression analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 54, 774–781 (2001).
Tian, X. P., Li, M. T. & Zeng, X. F. The challenges and opportunities for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in China: an annual report of 2019. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 60, 593–598 (2021).
Google Scholar
Shi, F. et al. Sample survey on the prevalence of arthritis in Shanghai and analysis of associated factors. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 72–76 (2003).
Syngle, D., Singh, A. & Verma, A. Impact of rheumatoid arthritis on work capacity impairment and its predictors. Clin. Rheumatol. 39, 1101–1109 (2020).
Google Scholar
Zhang, X. et al. The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on work capacity in Chinese patients: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol. (Oxford). 54, 1478–1487 (2015).
Google Scholar
Arleevskaya, M. et al. Interplay of environmental, individual and genetic factors in rheumatoid arthritis provocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 8140 (2022).
Google Scholar
Malysheva, O., Pierer, M., Wagner, U. & Baerwald, C. G. O. [Stress and rheumatoid arthritis]. Z. Rheumatol. 69, 539–543 (2010).
Google Scholar
Pamukcu, M., İzci Duran, T., Ulusoy, H. & Altınbaş, K. Investigation of the correlation between mood disorder symptoms and disease activity and functional status in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 51, 3008–3016 (2021).
Google Scholar
Yang, D. H., Huang, J. Y., Chiou, J. Y. & Wei, J. C.-C. Analysis of socioeconomic status in the patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 15, 1194 (2018).
Google Scholar
Ma, Y. et al. Correlation study between clinical symptoms and meteorological indicators in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with stable disease conditions. Chin. J. Disease Control. 19, 904–908 (2015).
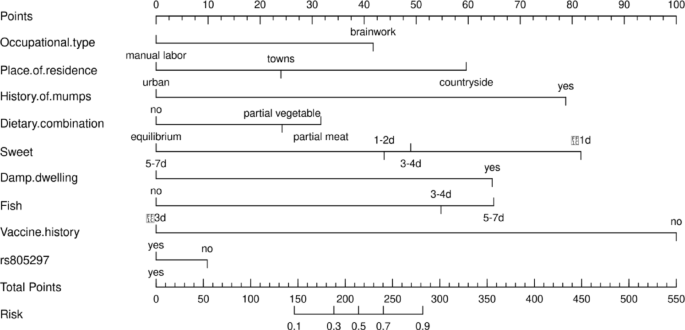
Huang, Y. et al. Apolipoprotein m (APOM) levels and APOM rs805297 G/T polymorphism are associated with increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 81, 32–36 (2014).
Google Scholar
Harrell, F. E. & Describing Resampling, Validating, and Simplifying the Model. in Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis (ed. Harrell, Jr., Frank E.) 103–126Springer International Publishing, Cham, (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19425-7_5
Doria, A., Zampieri, S. & Sarzi-Puttini, P. Exploring the complex relationships between infections and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 8, 89–91 (2008).
Google Scholar
Schmidt, R. E., Grimbacher, B. & Witte, T. Autoimmunity and primary immunodeficiency: two sides of the same coin? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 14, 7–18 (2018).
Google Scholar
Comee, L., Taylor, C. A., Nahikian-Nelms, M., Ganesan, L. P. & Krok-Schoen, J. L. Dietary patterns and nutrient intake of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in the united States. Nutrition 67–68, 110533 (2019).
Google Scholar
Cutolo, M. & Nikiphorou, E. Don’t neglect nutrition in rheumatoid arthritis! RMD Open. 4, e000591 (2018).
Google Scholar
Matsunaga, M., Lim, E., Davis, J. & Chen, J. J. Dietary quality associated with Self-Reported diabetes, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis among younger and older US adults: A Cross-Sectional study using NHANES 2011–2016. Nutrients 13, 545 (2021).
Google Scholar
Na, H. S. et al. Th17 and IL-17 cause acceleration of inflammation and fat loss by inducing α2-Glycoprotein 1 (AZGP1) in rheumatoid arthritis with High-Fat diet. Am. J. Pathol. 187, 1049–1058 (2017).
Google Scholar
Ma, X. et al. Excessive intake of sugar: an accomplice of inflammation. Front. Immunol. 13, 988481 (2022).
Google Scholar
Tedeschi, S. K. et al. Diet and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms: survey results from a rheumatoid arthritis registry. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken). 69, 1920–1925 (2017).
Google Scholar
Di Giuseppe, D., Wallin, A., Bottai, M., Askling, J. & Wolk, A. Long-term intake of dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study of women. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 1949–1953 (2014).
Google Scholar
Sparks, J. A. et al. Association of fish intake and smoking with risk of rheumatoid arthritis and age of onset: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 20, 2 (2019).
Google Scholar
Guo, M., Liu, X., Chen, X. & Li, Q. Insights into new-onset autoimmune diseases after COVID-19 vaccination. Autoimmun. Rev. 22, 103340 (2023).
Google Scholar
Orellana, C. et al. Oral contraceptives, breastfeeding and the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Swedish EIRA study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 76, 1845–1852 (2017).
Google Scholar
Seror, R. et al. Passive smoking in childhood increases the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. (Oxford). 58, 1154–1162 (2019).
Google Scholar